- Phone: (031) 849 5566
- WA: +6282140060234
- Email: [email protected]
- Hours: Mon-Fri, 8am - 5pm
Fraud Triangle: Uncovering the Issues and Practical Solutions
Fraud is a serious threat faced by many companies. These actions not only cause financial losses but also damage the company’s reputation and stakeholder trust. To prevent fraud effectively, organizations need to understand its root causes and establish the right internal controls.
Understanding The Fraud Triangle
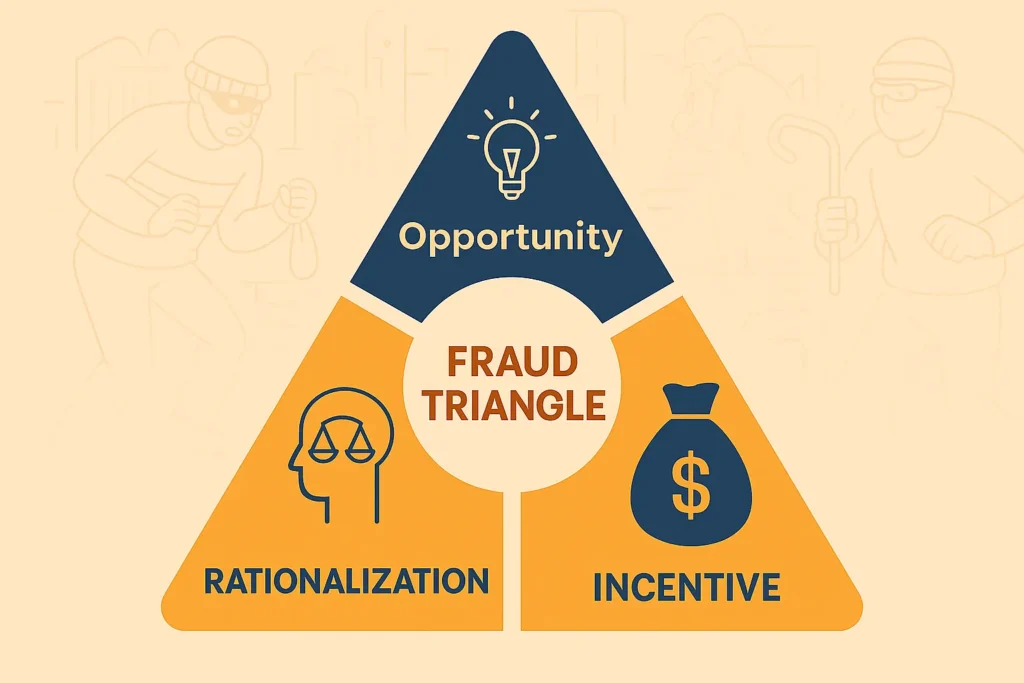
The ‘Fraud Triangle’ describes three main conditions that are almost always present when such misconduct occurs. This concept is widely explained in Auditing and Assurance Services (Arens, Elder, & Beasley, 2020):
“Three conditions are generally present when fraud occurs: incentive/pressure, opportunity, and attitude/rationalization.”
- Pressure / Incentive
Certain pressures or motivations that cause an individual to feel compelled to act outside acceptable boundaries. For example, pressure to meet sales targets, personal debt obligations, or the desire to maintain a particular lifestyle. - Opportunity
Conditions that allow fraudulent actions to be committed without easy detection. For Instance, the lack of segregation of duties, where a single person has full authority over recording transactions and approving payments. This gap significantly increases the risk of abuse. - Rationalization
The reasons an individual uses to justify their actions. For example, feeling unappreciated by the company or believing the act is merely “borrowing temporarily.”
Types of Fraud
In general, fraud in business falls into two main categories:
- Financial Statement Manipulation
Manipulating accounting records so financial reports appear better than reality, such as overstating revenue or hiding liabilities. - Asset Misappropriation
Theft of cash, inventory, or fictitious expenses committed by employees or other parties with access to company assets.
Practical Solutions
Preventing and addressing fraud is not only about identifying the perpetrators but also about ensuring the company has robust systems to minimize risks from the outset. An effective approach includes preventive measures, consistent detection efforts, and firm follow-up procedures. Here are several practical steps companies can implement to manage fraud risk more comprehensively:
Preventing Fraud
Prevention is key to closing potential fraud gaps. Some measures include:
- Establishing clear policies and procedures.
- Implementing proper segregation of duties so no single individual controls the entire transaction process.
- Conducting business ethics training to raise employee awareness.
Related: The Importance of Segregation of Duties in a Company’s Financial Functions
Detecting Fraud
If fraud has occurred or is suspected, companies should have systematic detection measures, such as:
- Regular document reviews and reconciliations.
- Risk-based internal audits.
- Secure whistleblowing channels for employees to report fraud.
Legal Action and Follow-Up
When fraud is confirmed, companies can take decisive steps:
- Collecting valid supporting evidence.
- Consulting with legal advisors.
- Reporting to authorities or pursuing legal processes as applicable.
Prompt and transparent action demonstrates the organization’s commitment to integrity.
PT SUN Role
As a business consultancy, PT SUN is ready to support your company in:
- Evaluation and Improvement of Internal Control Systems
Helping ensure that operational procedures are adequate and segregation of duties is effective. We also design policies tailored to your business characteristics to reduce potential gaps from the outset. - Business Ethics Training and Education
Equipping employees with an understanding of fraud risks, reporting obligations, and strengthening an integrity-driven workplace culture. This program is supported by the HR Synergy team, including experienced psychologists, to ensure the training materials are relevant, easy to understand, and capable of building sustainable ethical commitment.
Related: Understanding HR Fundamentals: Making HR Accessible to Everyone
- Gathering Fraud Evidence
Helping companies with document tracing, transaction reviews, and chronology preparation through agreed-upon procedures (AUP) in line with ISRS 4400 (Revised). The results are presented as factual findings without opinions or conclusions, providing a basis for management decisions or further legal action.
With the right approach, fraud risks can be minimized, and your company’s reputation can remain intact.
Contact Us for further consultation.
Reference:
Arens, A. A., Elder, R. J., & Beasley, M. S. (2020). Auditing and assurance services (16th ed.). Pearson.
IAASB. (2020). International Standard on Related Services (ISRS) 4400 (Revised): Agreed-Upon Procedures Engagements. International Federation of Accountants.





